The Tissue Level of Organization Is Best Described as ____
State whether the following describes epithelial connective muscle or nervous tissue. The micrograph that opens this chapter shows the high degree of organization among different types.

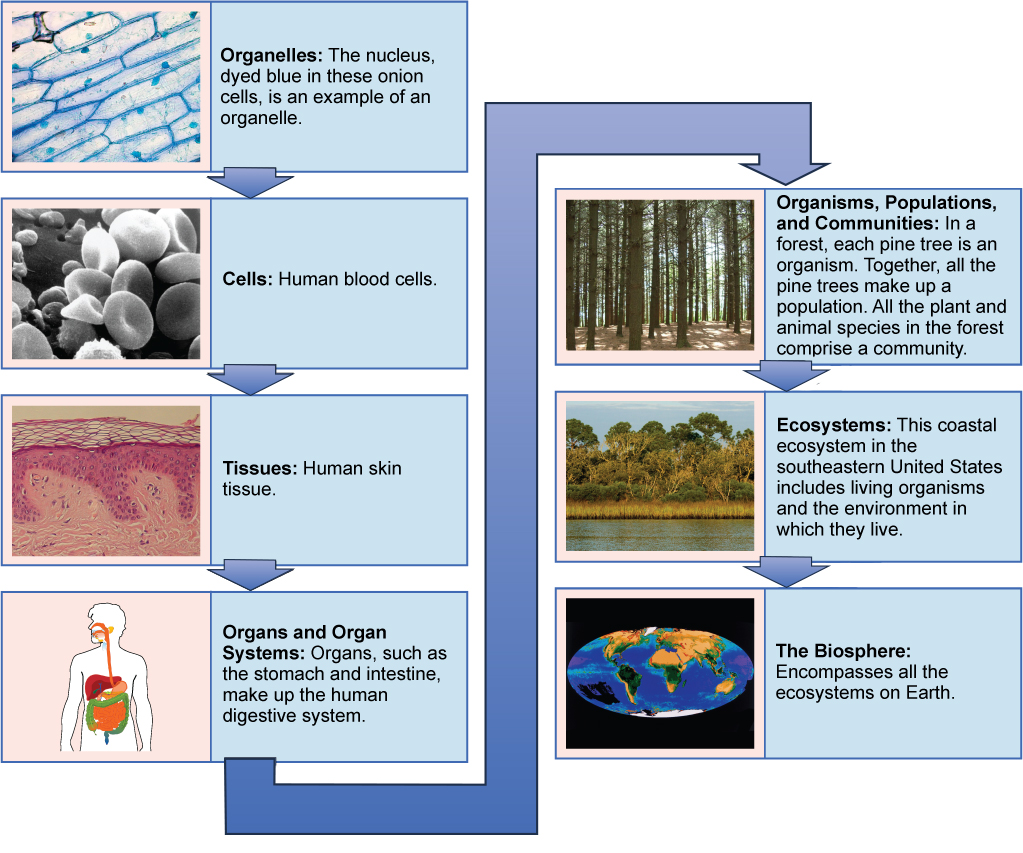
What Are The Levels Of Organization From Smallest To Largest At Level
Take up the quiz below on tissue level of organization to find out this and more.
. Makes up the majority of the brain and spinal cord - Nervous Tissue E. Stratified squamous epithelium loose connective dense connective tissue. Epithelial Tissue Epithelium An avascular layer of cells that forms a barrier that covers internal or external.
41 Identify the four types of tissues in the body and describe their roles. Poorly organized middle layer give rise to connective and most muscle tissues. Membranes that line cavities.
The Tissue Level of Organization Is Best Described as _____ Get link. Tissues which is not one of the four primary tissue types. Preview this quiz on Quizizz.
The Tissue Level of Organization Define the term tissue and classify the tissues of the body into four major types. Covers exposed surfaces lines internal passageways form glands. 44 Discuss the types and functions of intercellular connections between.
Epithelial tissue covers surfaces exposed to the environment skin airways digestive tracts glands 2. ____________ cover every exposed surface of the body and form the surface of. View Test Prep - Anatomy and Physiology_ Chapter 4 The Tissue Level Of Organization - Practice Quiz on Learningpodpd from ANATOMY 101 at University of Texas.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE. Tissue Level Of Organization Nonkeratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium Connective Tissue Proper Terms in this set 68 Groups of similar cells and extracellular products that carry out a common function are called. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
The Tissue Level of Organization. Which of these is the basic unit of life of all living things. Epithelial Tissue Learning Outcomes.
OTHER SETS BY THIS CREATOR. ECM is often the primary element - Connective Tissue B. The bone structure is made up of bone tissues compact and cancellous fibrous tissue hyaline cartilage and adipose tissue.
K - University grade. Tissue Level of Organization. AP Chapter 4 Review.
136 CHAPTER 4 THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION. Anatomy Chapter 4 Tissue Level of Organization 107 terms. Zoo Test 2 Ch 45.
Pathologist specialized in laboratory studies of cells and tissue for diagnoses. Review the material from this module by completing the practice test below. The central stage is described by the unrestrained creation of self-reactive cells and autoantibodies that occur because of the presence of antigens.
Consists of excitable cells that are specialized for contraction - Muscle Tissue C. Muscle tissue is specialized for contraction skeletal muscle heart muscle walls of hollow organs. The Tissue Level of Organization.
1 Skeletal muscle which forms the large muscles that produce gross body movements. Loose connective tissue incomplete layer of either squamous or cuboidal cells. Cells may be smooth.
Line the ventral body cavity. Membrane which surrounds joint cavities. Function in protection secretion absorption.
Stratified squamous epithelium loose connective dense connective tissue. 3 Smooth muscle found in the walls of visceral organs and a variety of tore locations where it provides elasticity contractility and support. Rather they occur in organized layers a level of organization referred to as tissue.
Which level of organization is a group of different tissues that work together to perform a function. -primarily concerned with secretion -typically arranged in a single layer of cells. 44 Discuss the types and functions of intercellular connections between.
42 Describe three microscopy techniques. What makes up a tissue. Tissue Level of Organization.
Inner layer develops into many different tissues including th linings of internal tubes of the body. Levels of Organization DRAFT. Other Apps -.
Body The four types of tissues are exemplified in nervous tissue stratified squamous epithelial tissue cardiac muscle tissue and connective tissue in small intestine. Cancellous Bone Research Paper. Overview of Tissue Science An Orientation to the Tissues of the Body Figure 4-1.
Test Your Understanding Saladin Ch. Connective tissue fills internal spaces supports other tissues transports materials and stores energy. Which of the following is NOT a basic type of tissue.
In observing epithelial cells under a microscope the cells are arranged in a single layer and look tall and narrow and the nucleus is located close to the basal side of the cell. What is a Tissue. Sheets of tightly packed cells with little ECM - Epithelial Tissue D.
Which statement best describes connective tissue. Start studying Anatomy Physiology - Tissue Level of Organization. Tissue that springs back like a rubber band to its normal length after being stretched.
43 Describe epithelial tissues including cell shape layers and functions. 136 CHAPTER 4 THE TISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION This content is available for free at Figure 42 Four Types of Tissue. Strongest cartilage in the body found in intervertebral discs.
A tissue is a group of cells Common embryonic origin Function together to carry out specialized activities Hard bone semisolid fat or liquid blood Histology is the science that deals with the study of tissues. 2018 Pearson Education Inc. Science 7 Levels Of Biological Organizations The Spectrum Of Biological Organization Youtube Epithelial Tissue Anatomy And Physiology Final Test Question Bank.
AP Ch 9 Tissue Types. The different types of cells are not randomly distributed throughout the body. 2 Cardiac muscle found in the heart is responsible for circulating the blood.
They differ based upon cells cytoskeleton ECM and junctions Types of junctions 1anchoring junctions 2tight junctions 3gap junctions. Licenses and Attributions. Weakest cartilage in the body that covers joint surfaces.
The specimen is what type of epithelial tissue. Nervous System and Nervous Tissue. Level of organization 1cells 2tissue 3organ 4organ system which is constantly evolving 5organism Types of animal tissue 1epithelial 2connective 3muscle 4nervous How can tissue differ.
The Tissue Level of Organization. The study of tissues is called ___________. _______________ are layers of cells that cover internal or external surfaces.
Specialized areolar tissue rich in stored fat. Muscle and nervous tissues will be discussed only briefly in this chapter. Mechanically attaches adjacent cells to each other or to the basement membrane.
That part of a cell or tissue which in general faces an open space.

Levels Of Organization Of Living Things Biology For Majors Ii

Levels Of Organization Biology Quiz Quizizz

Anatomy Chapter 4 Tissue Level Of Organization Flashcards Quizlet

No comments for "The Tissue Level of Organization Is Best Described as ____"
Post a Comment